Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections for Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
Introduction
Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment, also known as inferior calcaneal nerve entrapment, is a condition that can contribute to chronic heel pain. It is often misdiagnosed as plantar fasciitis due to the overlap in symptoms. The condition arises when the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, known as Baxter’s nerve, becomes compressed or irritated.
Anatomy of Baxter’s Nerve
Baxter’s nerve is a branch of the lateral plantar nerve, which originates from the tibial nerve. This small but significant nerve travels along the medial aspect of the heel and innervates the abductor digiti minimi muscle of the foot. Due to its anatomical course, Baxter’s nerve is prone to compression between the deep fascia of the abductor hallucis muscle and the medial calcaneal tuberosity.
Pathology and Causes of Entrapment
Baxter’s nerve entrapment occurs when the nerve is compressed or irritated due to various factors, including:
- Repetitive stress and overuse — Activities such as prolonged standing, running, or walking on hard surfaces can contribute to nerve compression.
- Biomechanical abnormalities — Flat feet (pes planus) or high arches (pes cavus) may alter foot mechanics and increase the risk of entrapment.
- Inflammation and fibrosis — Thickening of the plantar fascia or the presence of heel spurs can contribute to nerve irritation.
- Previous foot injuries — Fractures or soft tissue trauma around the heel can lead to scarring and entrapment.
- Obesity — Excess weight can increase pressure on the structures around Baxter’s nerve, leading to entrapment.
Symptoms of Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
The symptoms of Baxter’s nerve entrapment are often mistaken for other heel conditions such as plantar fasciitis. Common symptoms include:
- Medial heel pain that worsens with activity
- Pain that may radiate towards the lateral foot
- Burning, tingling, or numbness in the heel area
- Weakness in the abductor digiti minimi muscle, leading to subtle gait changes
- Pain that persists even with rest, unlike plantar fasciitis, which often improves with rest
Diagnosis of Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
A thorough clinical evaluation is essential to distinguish Baxter’s nerve entrapment from other causes of heel pain. Diagnosis may involve:
- Patient history and physical examination — Assessing pain distribution, tenderness over the nerve, and biomechanical factors.
- Imaging studies — Ultrasound can help identify nerve compression, soft tissue changes, or adjacent pathology such as plantar fasciitis or heel spurs.
Management of Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
Several conservative and interventional approaches can help manage Baxter’s nerve entrapment, including:
- Activity modification — Reducing repetitive stress activities that aggravate symptoms.
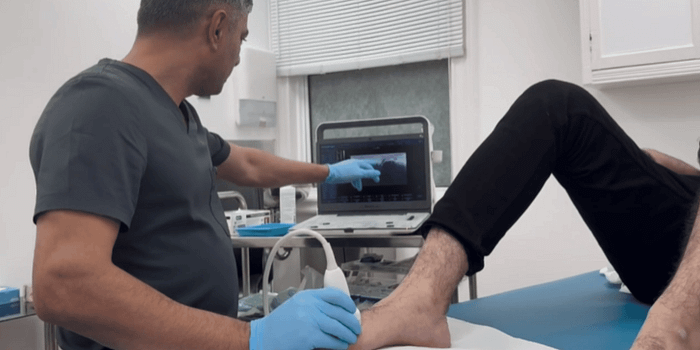
- Ultrasound-guided cortisone injections — A targeted approach to managing inflammation and alleviating symptoms.
Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections for Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
Ultrasound-guided cortisone injections are a minimally invasive option for managing Baxter’s nerve entrapment. By using real-time imaging, the injection can be precisely delivered to the site of entrapment, reducing inflammation and alleviating pain.
Benefits of Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections
- Precise targeting — Ensures accurate placement of the injection near the affected nerve.
- Minimised complications — Reduces the risk of injecting into surrounding structures.
- Reduced inflammation — Helps alleviate nerve irritation and associated pain.
- Quick procedure — Can be performed in an outpatient setting with minimal downtime.
Mechanism of Action of Cortisone
Cortisone is a corticosteroid that works by reducing inflammation and suppressing immune responses in the targeted area. When injected near Baxter’s nerve:
- It decreases local inflammation around the nerve, reducing pressure and irritation.
- It inhibits inflammatory mediators, helping to relieve pain and swelling.
- It may improve mobility and function by reducing discomfort associated with nerve compression.
Why Choose Joint Injections for This Treatment?
At Joint Injections, we specialise in ultrasound-guided procedures to ensure precise and effective treatment. Our approach includes:
- Experienced specialists — Experts in ultrasound-guided musculoskeletal injections.
- Advanced imaging techniques — Real-time ultrasound for accurate placement.
- Patient-centred care — A tailored approach to meet individual treatment needs.
Conclusion
Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment is an under-recognised cause of chronic heel pain that can significantly impact daily activities. While conservative treatments can be effective, ultrasound-guided cortisone injections offer a targeted approach to managing inflammation and alleviating symptoms. By reducing nerve irritation and improving function, these injections may be a valuable option for individuals experiencing persistent heel pain. Joint Injections provides precise, patient-focused care, ensuring effective treatment tailored to individual needs.
Comments
Post a Comment