Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections for Heel Bursitis
Introduction
Heel bursitis is a condition that affects the bursae, which are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. Inflammation of these bursae in the heel region can result in significant pain and discomfort, impacting daily activities such as walking, running, and standing for extended periods.
Heel bursitis can occur due to repetitive stress, excessive pressure, or biomechanical abnormalities. While various treatment options exist, ultrasound-guided cortisone injections have been used to target inflammation with precision.
Anatomy of the Heel
The heel is a complex structure composed of bones, soft tissues, and bursae. Key anatomical components include:
- Calcaneus (heel bone) — The largest bone in the foot, responsible for weight-bearing.
- Achilles tendon — Connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a crucial role in movement.
- Retrocalcaneal bursa — Located between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus, reducing friction during movement.
- Subcutaneous calcaneal bursa — Positioned between the skin and the Achilles tendon to minimise pressure.
- Plantar fascia — A thick band of tissue running along the sole, supporting the arch of the foot.
When bursae become inflamed, they can cause pain, swelling, and mobility restrictions.
Pathology of Heel Bursitis
Heel bursitis develops when excessive stress, friction, or trauma leads to irritation and inflammation of the bursae. Two main types of heel bursitis include:
- Retrocalcaneal Bursitis — Affects the bursa located between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus. Often associated with repetitive strain, improper footwear, or excessive physical activity.
- Subcutaneous Calcaneal Bursitis — Involves inflammation of the bursa between the skin and Achilles tendon, often resulting from prolonged pressure on the heel.
Causes of Heel Bursitis
Several factors can contribute to the development of heel bursitis, including:
- Overuse or repetitive strain (e.g., running, jumping, or excessive walking)
- Poorly fitting footwear (tight shoes, high heels, or rigid soles)
- Biomechanical issues (flat feet, high arches, or abnormal gait)
- Direct trauma to the heel (such as impact injuries or excessive pressure)
- Inflammatory conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout)
Symptoms of Heel Bursitis
Common symptoms of heel bursitis include:
- Pain and tenderness around the heel, especially at the back
- Swelling and redness in the affected area
- Increased discomfort with movement or pressure
- Stiffness and reduced flexibility in the foot and ankle
- Warmth over the inflamed bursa
Diagnosis of Heel Bursitis
A thorough clinical assessment is essential for diagnosing heel bursitis. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Medical History: Evaluation of symptoms, lifestyle, and possible triggers.
- Physical Examination: Checking for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Provides real-time imaging to assess inflammation and fluid accumulation.
Management of Heel Bursitis
Various conservative and interventional approaches may be considered for managing heel bursitis.
Conservative Treatment
Initial management typically includes:
- Rest and activity modification to reduce strain on the heel.
- Ice therapy to help control inflammation.
- Proper footwear and orthotics to relieve pressure.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve foot mechanics.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections for Heel Bursitis
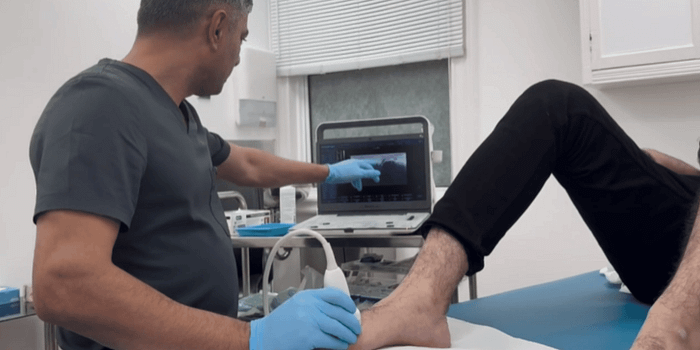
When symptoms persist despite conservative measures, ultrasound-guided cortisone injections may be considered. These injections are designed to target the inflamed bursa with precision, potentially aiding in pain reduction and symptom management.
Benefits of Ultrasound Guidance
- Real-time visualisation ensures accurate needle placement.
- Minimises risk of injection into surrounding structures.
- Enhances precision in delivering cortisone to the inflamed bursa.
- Reduces discomfort associated with improper injection techniques.
Mechanism of Action of Cortisone for Heel Bursitis
Cortisone is a synthetic corticosteroid that mimics the body’s natural anti-inflammatory hormones. It works through the following mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Inflammatory Mediators:
- Cortisone reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes responsible for swelling and pain.
2. Suppression of Immune Response:
It modulates immune activity within the bursa, potentially decreasing excessive inflammation.
3. Reduction of Vascular Permeability:
- Helps to limit fluid accumulation, which contributes to swelling and discomfort.
4. Stabilisation of Cell Membranes:
- Prevents further irritation and injury to bursal tissues.
Why Choose Ultrasound-Guided Cortisone Injections at Joint Injections?
At Joint Injections, ultrasound guidance is used to enhance accuracy and precision when administering cortisone injections. Potential benefits include:
- Targeted administration with real-time imaging.
- Minimised risk of injecting into unintended areas.
- Reduced discomfort compared to blind injections.
- Specialist care tailored to musculoskeletal conditions.
Post-Injection Care and Rehabilitation
Following an ultrasound-guided cortisone injection, aftercare may involve:
- Short-term activity modification to avoid excessive pressure on the heel.
- Gradual return to normal activities with guided rehabilitation exercises.
- Footwear adjustments to prevent recurrent bursitis.
Conclusion
Heel bursitis can cause significant discomfort and impair daily function. While conservative management plays an important role, ultrasound-guided cortisone injections may be considered to aid in symptom management. By precisely targeting inflammation, this approach may help address pain and discomfort in cases where other interventions have not provided sufficient relief.
At Joint Injections, advanced imaging techniques are used to administer cortisone injections with accuracy, supporting a comprehensive approach to musculoskeletal care.
Comments
Post a Comment